Engineering Workflows on Azure
Advanced Data Engineering Workflows on Azure with DVC, Airflow, and MLflow
Fedi HAMDI
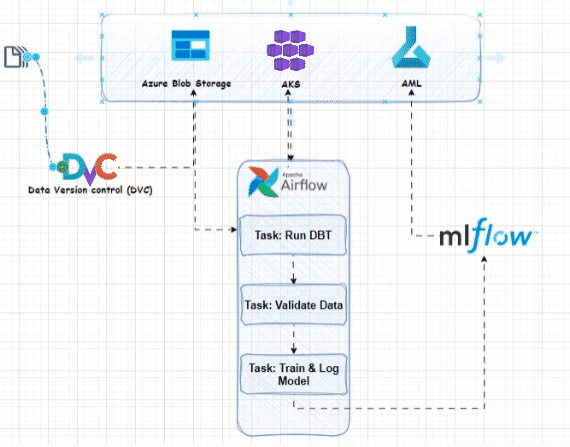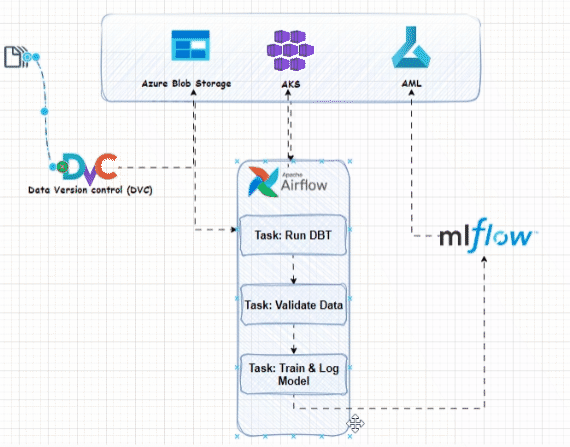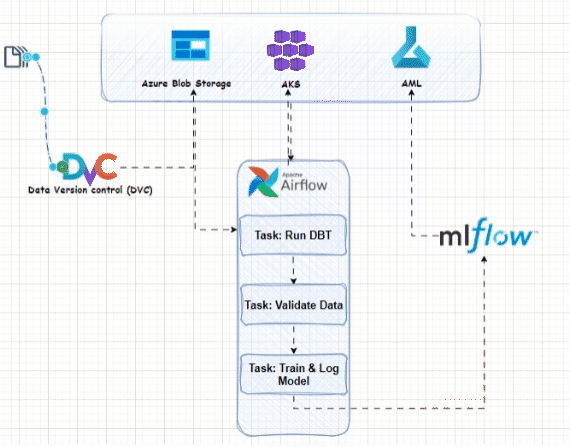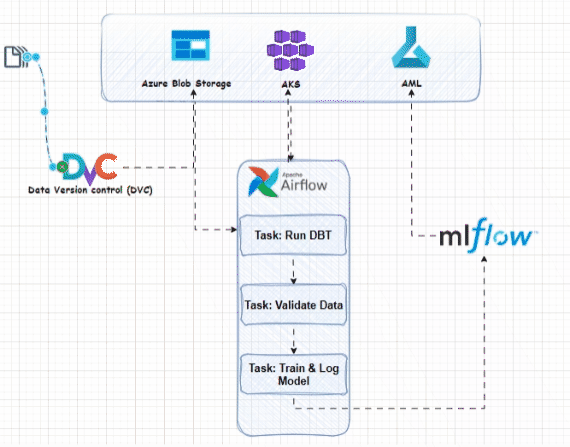
In the fast-paced world of data engineering, mastering advanced tools and leveraging the power of the cloud can significantly enhance your workflow and productivity. While DBT and Python provide a solid foundation for data transformation, integrating tools like DVC, Airflow, and MLflow on Azure can elevate your workflows to an expert level. This article will delve into using these powerful tools to create a robust, scalable, and efficient data transformation process on Azure. Let's dive into the world of DVC, Airflow, and MLflow on Azure!
Recap: DBT and Python Synergy
Before we leap into advanced tools, let’s briefly revisit the synergy between DBT and Python. DBT (Data Build Tool) excels in SQL-based data transformations, and Python adds flexibility and power, enabling complex validations, preprocessing, and machine learning integrations. Building on this foundation, we’ll explore how DVC, Airflow, and MLflow can further enhance your data workflows on Azure.
For more please visit : DVC article
Advanced Data Version Control with DVC on Azure
Data Version Control (DVC) extends Git-like version control to datasets, models, and intermediate data, ensuring reproducibility and collaboration across your projects. Azure Blob Storage can be used as remote storage for your data files.
Setting Up DVC on Azure
-
Install DVC:
pip install dvc -
Initialize DVC in Your Project:
dvc init -
Track Your Data Files:
dvc add data/raw/customers.csv dvc add data/processed/validated_customers.csv -
Commit the Changes:
git add data/.gitignore data/raw/customers.csv.dvc data/processed/validated_customers.csv.dvc git commit -m "Track raw and processed data with DVC" -
Configure Azure Blob Storage:
-
Set up an Azure Blob Storage account and container.
-
Configure DVC to use Azure Blob Storage as the remote storage:
dvc remote add -d myremote azure://mycontainer/path
-
-
Authenticate with Azure:
-
Install the Azure CLI and authenticate:
az login
-
-
Push Your Data to Azure Blob Storage:
dvc push
Orchestrating Workflows with Apache Airflow on Azure
Apache Airflow is a powerful platform for authoring, scheduling, and monitoring workflows, making it ideal for managing complex data pipelines. Running Airflow on Azure ensures scalability and reliability.
Setting Up Airflow on Azure
-
Deploy Airflow on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS):
-
Create an AKS cluster:
az aks create --resource-group myResourceGroup --name myAKSCluster --node-count 1 --enable-addons monitoring --generate-ssh-keys -
Connect to your AKS cluster:
az aks get-credentials --resource-group myResourceGroup --name myAKSCluster -
Deploy Airflow using Helm:
helm repo add apache-airflow https://airflow.apache.org helm repo update helm install airflow apache-airflow/airflow --namespace airflow --create-namespace
-
-
Create a DAG: Define a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) to orchestrate your workflow.
from airflow import DAG from airflow.operators.bash_operator import BashOperator from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator from datetime import datetime default_args = { 'owner': 'airflow', 'depends_on_past': False, 'start_date': datetime(2024, 6, 18), 'retries': 1, } dag = DAG( 'dbt_python_workflow', default_args=default_args, schedule_interval='@daily', ) run_dbt = BashOperator( task_id='run_dbt', bash_command='dbt run', dag=dag, ) def validate_data(): import scripts.data_validation as dv dv.validate_data() run_validation = PythonOperator( task_id='run_validation', python_callable=validate_data, dag=dag, ) run_dbt >> run_validation -
Access the Airflow UI:
kubectl port-forward svc/airflow-webserver 8080:8080 --namespace airflow
Advanced Orchestration Techniques
- Dynamic DAGs: Use dynamic DAGs to create workflows that adapt based on external inputs or configurations.
- Task Dependencies: Manage complex dependencies between tasks to ensure proper execution order.
- Error Handling: Implement robust error handling and alerting to address failures in your workflow.
Managing the ML Lifecycle with MLflow on Azure
MLflow provides an open-source platform to manage the end-to-end machine learning lifecycle, from experimentation to deployment. Using Azure Machine Learning (AML) and Azure Blob Storage, you can enhance MLflow’s capabilities.
Setting Up MLflow on Azure
-
Install MLflow:
pip install mlflow -
Configure Azure ML:
-
Set up an Azure ML workspace.
-
Authenticate with Azure ML:
az login az ml workspace create -n myWorkspace -g myResourceGroup
-
-
Track Experiments: Log parameters, metrics, and models within your Python scripts.
import mlflow import mlflow.azureml mlflow.set_tracking_uri("azureml://<YOUR_AZUREML_WORKSPACE_URI>") mlflow.start_run() # Parameters mlflow.log_param("param1", value) # Metrics mlflow.log_metric("metric1", value) # Model mlflow.log_artifact("model.pkl") mlflow.end_run() -
Integrate with Airflow: Add MLflow tracking to your Airflow DAG to monitor model performance over time.
def train_and_log_model(): import mlflow # Training and logging code here train_model = PythonOperator( task_id='train_model', python_callable=train_and_log_model, dag=dag, ) run_dbt >> run_validation >> train_model
Advanced MLflow Features
- Model Registry: Use MLflow’s model registry to manage and deploy models.
- Experiment Tracking: Compare experiments, visualize results, and manage model versions.
- Deployment: Deploy models to various environments (e.g., Azure Kubernetes Service, Azure Container Instances) seamlessly.
Putting It All Together
Here’s an advanced project structure incorporating DVC, Airflow, and MLflow on Azure:
my_dbt_project/
├── data/
│ ├── raw/
│ │ └── customers.csv
│ ├── processed/
│ │ └── validated_customers.csv
├── models/
│ ├── staging/
│ │ └── stg_customers.sql
│ ├── marts/
│ │ └── customers/
│ │ └── customer_orders.sql
├── tests/
│ └── assert_customer_data.sql
├── macros/
│ └── my_custom_macro.sql
├── scripts/
│ └── data_validation.py
├── dags/
│ └── dbt_python_workflow.py
├── mlruns/ (auto-created by MLflow)
├── dvc.yaml
├── dbt_project.yml
└── README.mdConclusion
Integrating DVC, Airflow, and MLflow with your DBT and Python workflows on Azure transforms your data engineering capabilities, providing robust version control, efficient workflow orchestration, and comprehensive machine learning lifecycle management. These tools offer a powerful, scalable, and maintainable approach to handling complex data workflows, empowering you to achieve new heights in data engineering.
Additional Resources
- DBT Documentation
- DVC Documentation
- Airflow Documentation
- MLflow Documentation
- Azure ML Documentation
- Repo containing the code
- Portfolio
Fedi HAMDI